建设企业网站企业网上银行登录官网推介网
接上篇《9、流程控制语句-条件语句(if-else)》
上一篇我们学习了Python的控制流语句的概念,以及其中的条件语句(if/else),本篇我们来学习控制流语句中的循环语句(for/while)。
一、Python中的循环
Python的循环结构就是让程序“杀个回马枪”,不断地重复执行同一段代码。Python中的循环语句有2种,分别是for循环和while循环,我们下面一一来进行讲解。
二、for循环
1、语法格式
for 循环的语法格式如下:
for 迭代变量 in 字符串|列表|元组|字典|集合:代码块语法中的迭代变量,就是用来存放从后面的序列类型的集合中取出来的单个元素。代码块是用来进行循环调用的代码,也被成为循环体。
for语句的大致执行流程图如下所示: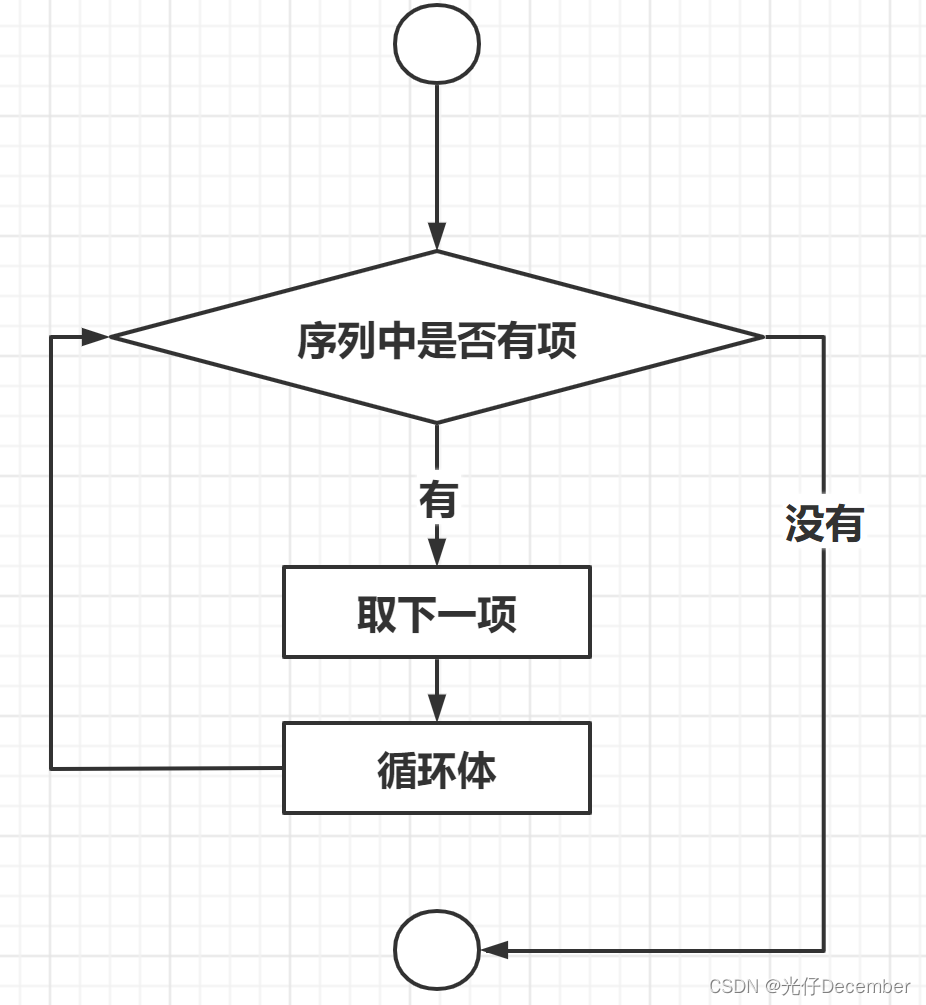
2、核心功能
for循环最重要的也是最核心的功能就是遍历,坦白点说就是一个一个的输出。例如下面这个例子,我们想一个个的打印python字符串的每一个字符,如果没有for循环,是这样的:
s = "python"
print("第1个字符是:",s[0])
print("第2个字符是:",s[1])
print("第3个字符是:",s[2])
print("第4个字符是:",s[3])
print("第5个字符是:",s[4])
print("第6个字符是:",s[5])效果:
第1个字符是: p
第2个字符是: y
第3个字符是: t
第4个字符是: h
第5个字符是: o
第6个字符是: n这样固然是可以全部遍历,但是如果有一百个或一万个字符呢?所以我们要是用简便的方法来循环内容。
有了for循环,就可以在for循环的代码块中不停的循环遍历:
s = "python"
i = 1
for ch in s:print(f"第{i}个字符是:", ch)i+=1效果:
第1个字符是: p
第2个字符是: y
第3个字符是: t
第4个字符是: h
第5个字符是: o
第6个字符是: n这里只需要编写一个for循环结构即可解决这个问题。
3、遍历列表和元组
当用for循环遍历list列表或者tuple元组时,其迭代变量会先后被赋值为列表或元组中的每个元素并执行一次循环体。实例:
#列表
test_list = [110,120,119]
for n in test_list:print("n = ",n)#元组
test_tuple = (66,88,99)
for m in test_tuple:print("m = ",m)效果:
n = 110
n = 120
n = 119
m = 66
m = 88
m = 99如果我们想获取列表的下标,可以利用range函数,这里介绍一下range函数,range()函数能够轻松地生成一系列的数字,格式:
range(开始数字,结束数字) 或 range(结束数字)range()函数的用法是:让Python从指定的第一个值开始,一直数到指定的第二个值停止,但不包含第二个值。如果参数仅有一个数字,则默认从0开始遍历。
比如:
>>> list(range(1,6))
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]注意:range()函数的返回值类型为range,并不直接是列表类型(list),而如果想要得到range()函数创建的数字列表,需要借助list()函数。
range还可以指定步长,格式:
range(开始数字,结束数字,步长)函数range()从“开始数字”开始数,然后不断地加“步长”数字,直到达到或超过终值“结束数字”。
比如:
>>> n = list(range(2,11,2))
>>> print(n)
[2, 4, 6, 8, 10]所以我们借助这个思路,可以思考一下,一般list列表或者tuple元组的长度都是从0开始,然后到len(列表或元组)结束(len()函数用于计算列表等多元素集合的长度),所以获取列表或元组的所有下标的函数应写为:
range(0,len(列表或元组变量名))所以当上面的代码需要打印下标的时候,代码为:
#列表
test_list = [110,120,119]
for i in range(0,len(test_list)):print(f"test_list[{i}] = ",test_list[i])#元组
test_tuple = (66,88,99)
for j in range(0,len(test_tuple)):print(f"test_tuple[{j}] = ",test_tuple[j])效果:
test_list[0] = 110
test_list[1] = 120
test_list[2] = 119
test_tuple[0] = 66
test_tuple[1] = 88
test_tuple[2] = 994、遍历字典
如果使用for循环直接遍历字典,则迭代变量会被先后赋值为每个键值对中的键,如下:
per_con = {'姓名': "光仔December",'年龄': "30岁",'学校': "河南理工大学"}
for ele in per_con:print('ele =', ele)结果:
ele = 姓名
ele = 年龄
ele = 学校在使用for循环遍历字典时,经常会用到和字典相关的3个方法,即items()、keys()以及values(),其中items()是每个键值对元素,keys()是键,values()是值,所以可以这样获取字典中的每个元素、每个元素的键,每个元素的值:
per_con = {'姓名': "光仔December",'年龄': "30岁",'学校': "河南理工大学"}
for ele in per_con.items():print('键值对元素 =', ele)
for key,value in per_con.items():print(f'key = {key},value = {value}')
for ele in per_con.keys():print('元素的key =', ele)
for ele in per_con.values():print('元素的value =', ele)结果:
键值对元素 = ('姓名', '光仔December')
键值对元素 = ('年龄', '30岁')
键值对元素 = ('学校', '河南理工大学')
key = 姓名,value = 光仔December
key = 年龄,value = 30岁
key = 学校,value = 河南理工大学
元素的key = 姓名
元素的key = 年龄
元素的key = 学校
元素的value = 光仔December
元素的value = 30岁
元素的value = 河南理工大学三、while循环
while循环和if条件分支语句类似,即在条件(表达式)为真的情况下,会执行相应的代码块。不同之处在于,只要条件为真,while就会一直重复执行那段代码块。语法格式如下:
while 条件表达式:代码块这里的代码块,指的是缩进格式相同的多行代码,不过在循环结构中,它又称为循环体。
while语句执行的具体流程为:首先判断条件表达式的值,其值为真(True)时,则执行代码块中的语句,当执行完毕后,再回过头来重新判断条件表达式的值是否为真,若仍为真,则继续重新执行代码块...如此循环,直到条件表达式的值为假(False),才终止循环。执行流程如下图所示: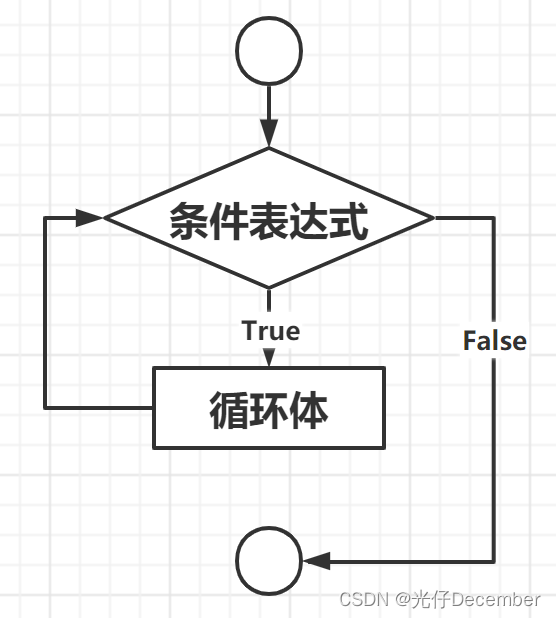
如打印10以内的所有偶数就可以使用while循环,代码如下:
# 循环的初始化条件
num = 1
# 当 num 小于10时,会一直执行循环体
while num < 10 :if num%2==0 :print("num=", num)else:print("*****")# 迭代语句num += 1
print("循环结束!")效果:
*****
num= 2
*****
num= 4
*****
num= 6
*****
num= 8
*****
循环结束!注意,在使用while循环时,一定要保证循环条件有变成假的时候,否则这个循环将成为一个死循环。所谓死循环,指的是无法结束循环的循环结构,例如将上面while循环中的num+=1代码注释掉,再运行程序你会发现,Python解释器一直在输出"*****",永远不会结束(因为num<10一直为True),除非我们强制关闭解释器: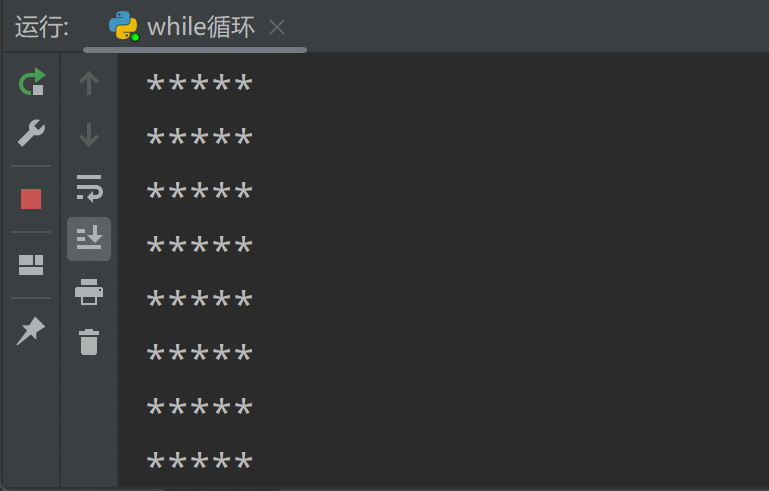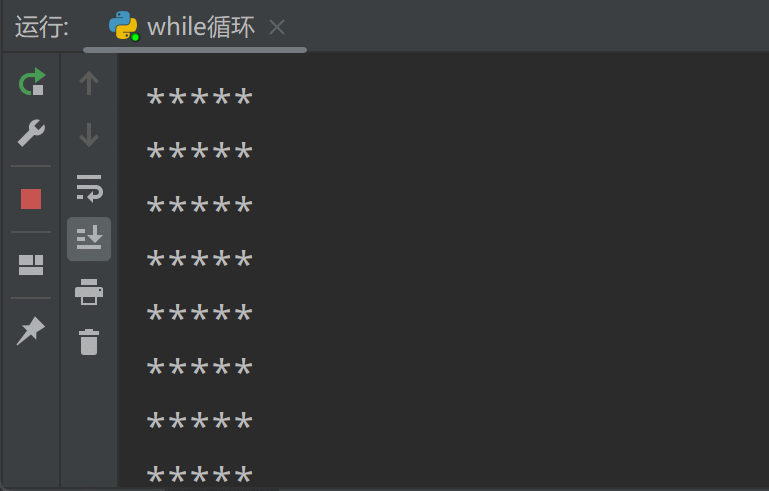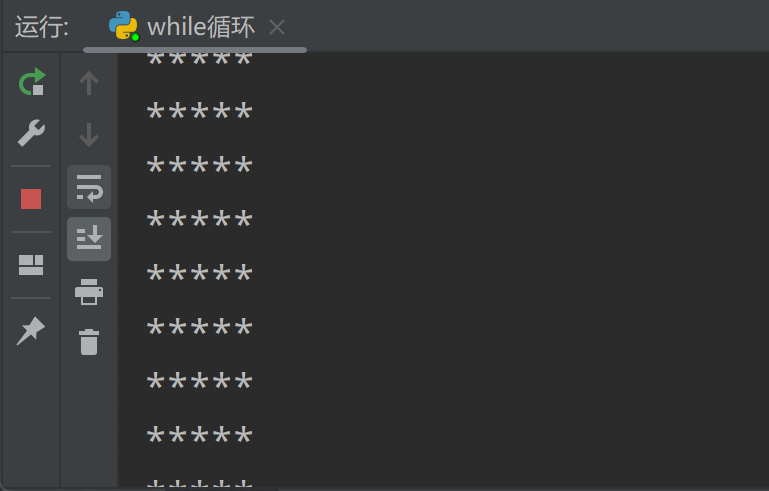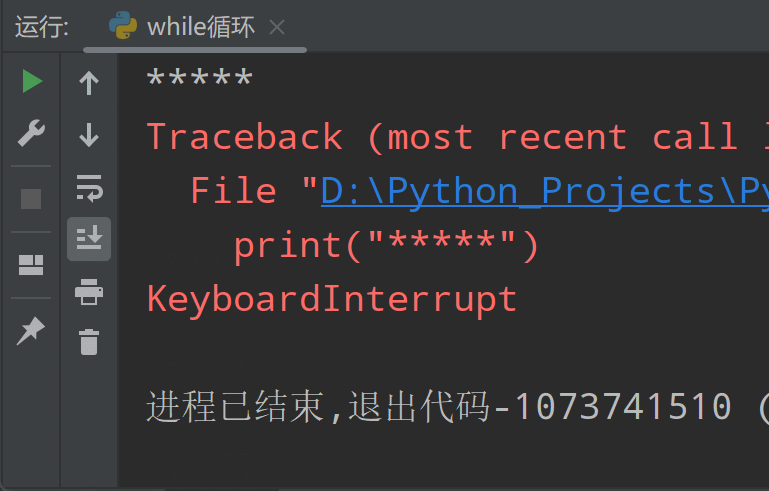
除此之外,while循环还常用来遍历列表、元组和字符串,因为它们都支持通过下标索引获取指定位置的元素。
代码示例:
#遍历字符串
my_char="python"
i = 0
while i<len(my_char):print(f"my_char[{i}]:",my_char[i])i = i + 1
#遍历列表和元组
test_list = [110,120,119]
i = 0
while i<len(test_list):print(f"test_list[{i}]:",test_list[i])i = i + 1
test_tuple = (66,88,99)
i = 0
while i<len(test_tuple):print(f"test_tuple[{i}]:",test_tuple[i])i = i + 1效果:
my_char[0]: p
my_char[1]: y
my_char[2]: t
my_char[3]: h
my_char[4]: o
my_char[5]: n
test_list[0]: 110
test_list[1]: 120
test_list[2]: 119
test_tuple[0]: 66
test_tuple[1]: 88
test_tuple[2]: 99至此,有关Python的流程控制语句所有内容内容就讲解完毕了,下一篇我们继续来学习字符串的高级应用。
参考:尚硅谷Python爬虫教程小白零基础速通教学视频
转载请注明出处:https://blog.csdn.net/acmman/article/details/129349447
