泸州市建设工程质量监督站网站汉字域名的网站
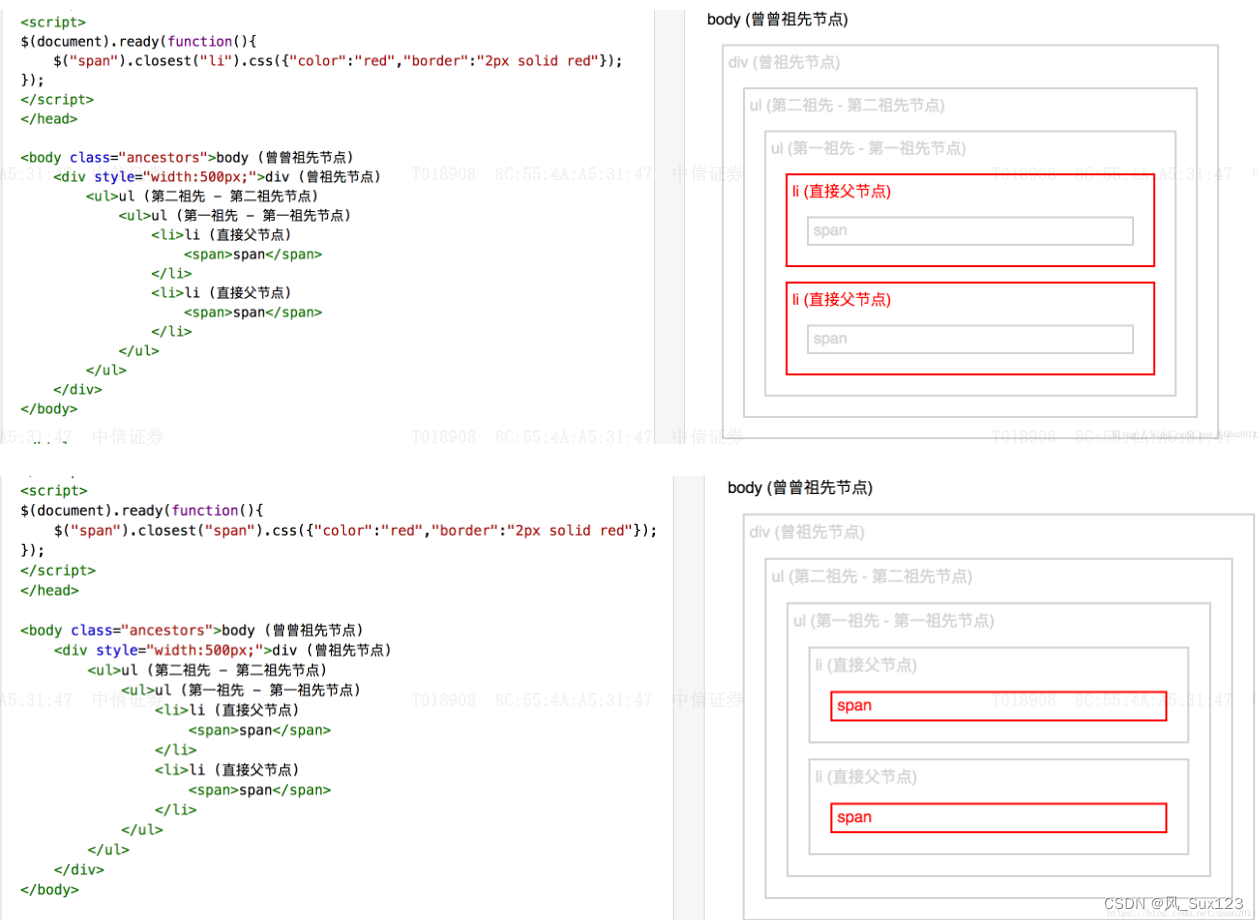
closest()是一个非常好用的查找祖先对象的方法,它和parent()和parents()相比,优点是简洁直观,返回0或1个对象,避免了返回很多对象而不知道怎么处理的尴尬,查找的是满足一定条件下的第一个祖先
var tbl = $(obj).closest("table");
这句js的意思是找到obj对象的第一个table祖先元素,这里的obj可以是tr,tbody,td,td或tr里面的input,等等元素标签
.closest()
1.从当前元素开始
2.遍历DOM树直到找到与提供的选择器匹配的元素
3.遍历原始集合中的每一个元素,返回包含零个或一个元素的jQuery对象,返回元素的顺序与文档顺序保持一致
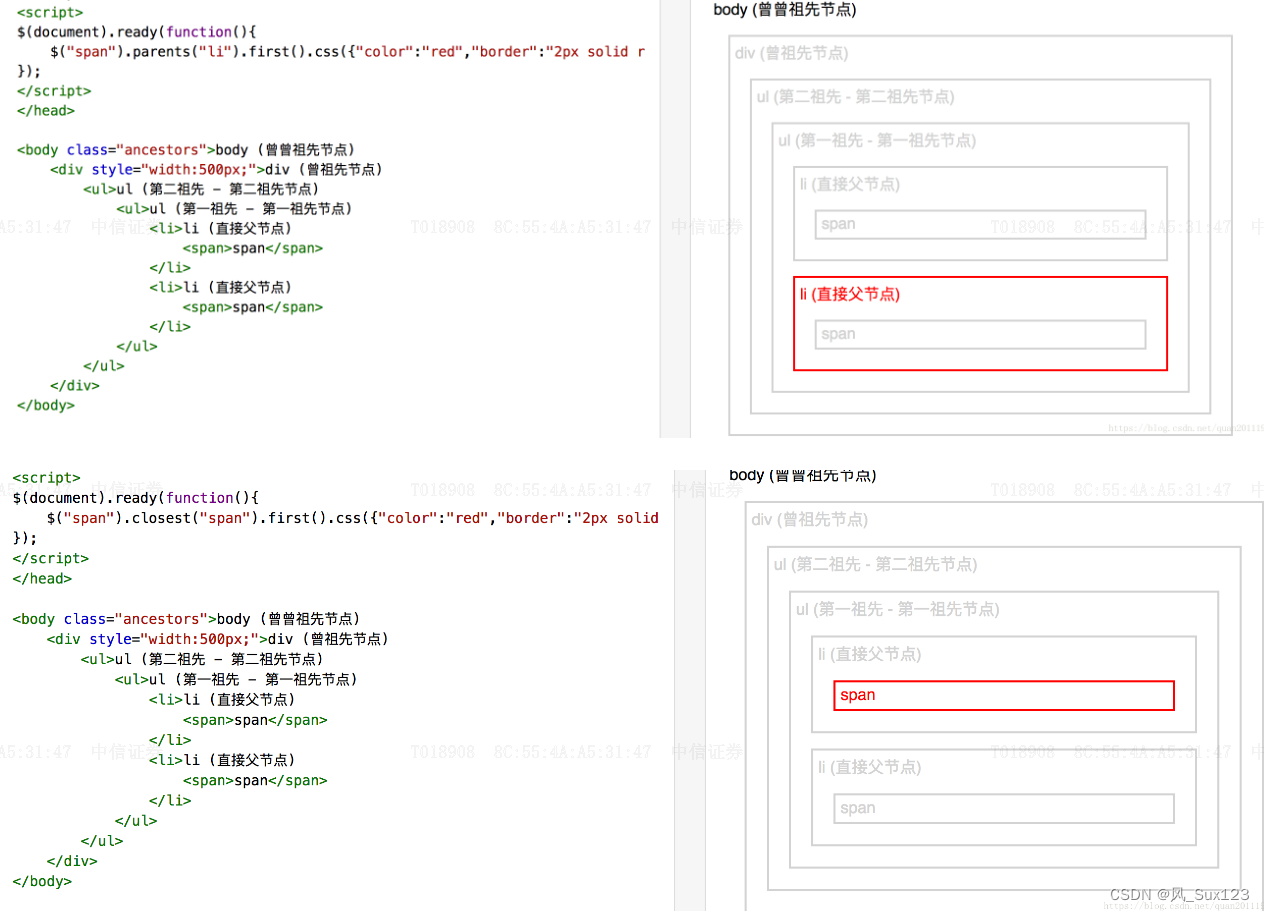
.parents()
1.从父元素开始
2.遍历DOM树到达文档的根元素,添加每一个祖先元素到临时的集合中,如果提供的选择器则基于这个选择器过于临时的集合
3.遍历原始集合中的每一个元素,返回包含零个或多个元素的jQuery对象,返回元素的顺序与文档顺序相反