泰州专业网站建设制作个人网站制作毕业设计选题重难点
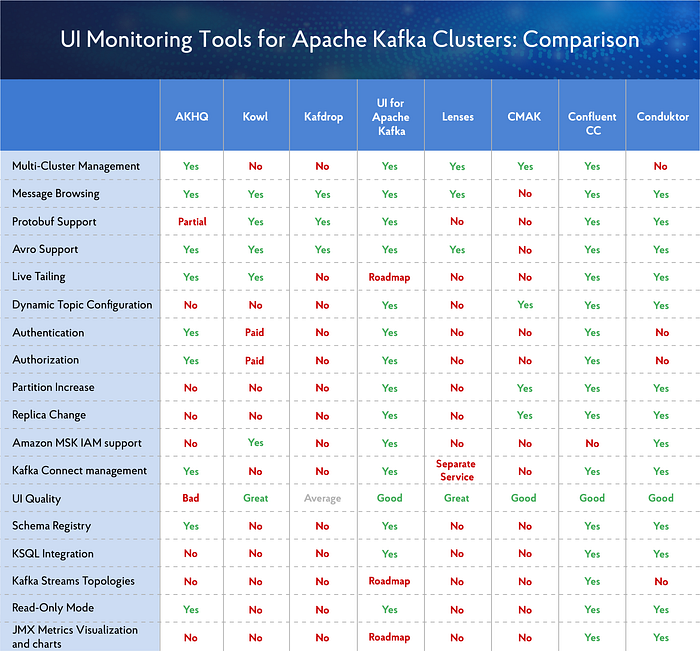
文章Overview of UI Tools for Monitoring and Management of Apache Kafka Clusters | by German Osin | Towards Data Science中介绍了8种常见的kafka UI工具,这些产品的核心功能对比信息如下图所示, 通过对比发现 UI for Apache Kafka 功能齐全且免费,因此可以作为我们的首选。本文通过二进制jar包的方式进行安装测试。
下载
从 https://github.com/provectus/kafka-ui/releases 下载最新版jar包。
[root@slave02 kafka-ui]# ls
kafka-ui-api-v0.7.1.jar
配置
在家目录下新建配置文件 application-local.yml ,配置内容如下:
kafka