综合类门户网站有哪些网站开发 需求文档
引言
如果能像解读一本神秘的书籍那样,理解DNA的“语言”,将是多么令人兴奋的科学突破!如今,这正在逐步变为现实。科学家们训练出的AI模型GROVER正如一个勤奋的学生,学习着DNA的每一个“单词”和“语法”,揭开生命代码的秘密面纱。

来源:《自然:机器智能》
01
AI模型GROVER
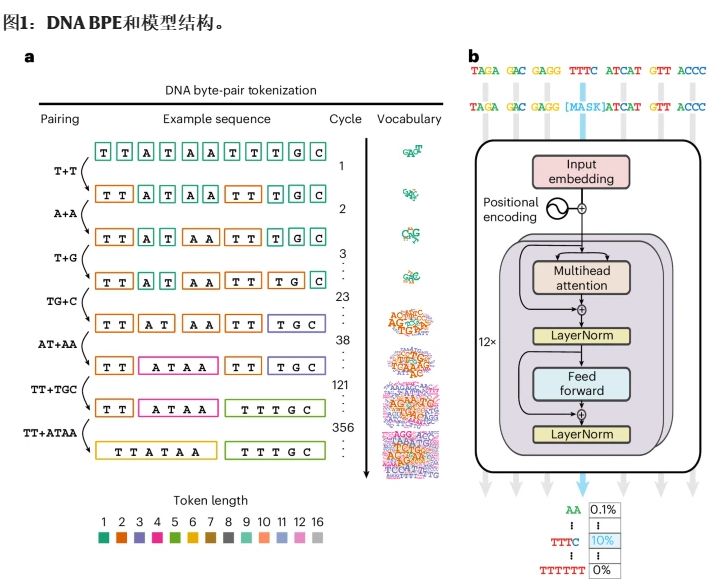
科学家们将DNA视作一种语言,而GROVER就是学习这种语言的AI。通过深度学习,GROVER能够理解DNA序列的模式,就像GPT模型理解人类语言一样。
它不仅能够预测DNA序列,还能识别出基因启动子或蛋白质结合位点,这些是控制基因表达的关键元素。
02
“表观遗传”
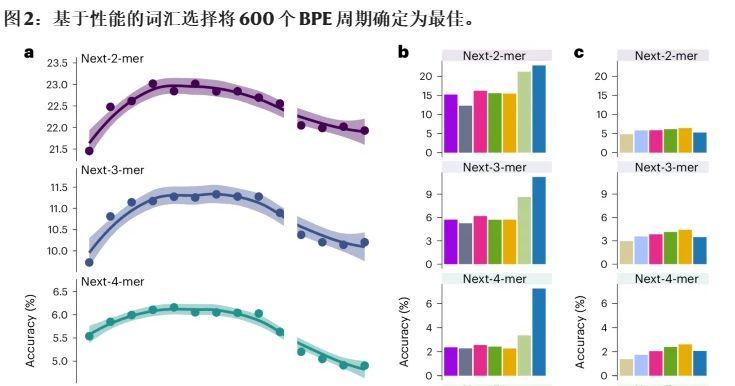
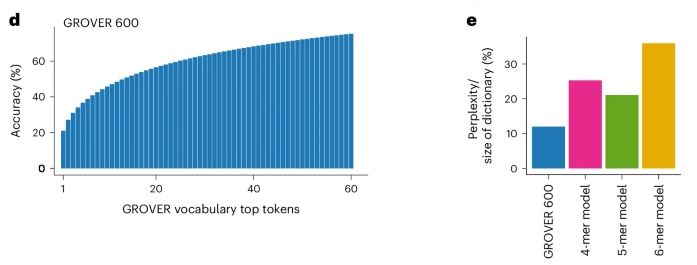
GROVER还学会了“表观遗传”这一概念。即使DNA序列不变,基因表达也会发生可遗传的变化,这正是表观遗传学研究的焦点。
GROVER通过学习,能够识别出这些变化的模式,为科学家们提供了一个全新的视角,来探索基因表达的复杂机制。
03
AI解锁生命之谜
通过语言模型理解DNA的规则,AI有望解锁DNA中蕴含的关于人类本质的关键信息。这不仅能够加深我们对遗传学的理解,还可能在疾病诊断、治疗和基因编辑技术的发展上,带来革命性的突破。
结论
AI模型GROVER的学习之旅,正引领我们进入一个全新的科学领域,一个AI和生物科学交汇的未来。随着技术的不断进步,我们期待AI将如何继续解锁生命的奥秘,为人类健康和福祉带来更多的可能性。
