【项目背景】
跳绳是一个很好的健身项目,为了获知所跳个数,有的跳绳上会有计数器。但这也只能跳完这后看到,能不能在跳的过程中就能看到,这样能让我们坚持跳的更多,更有趣味性。
【项目设计】
通过Mind+Python模式下加载Google的开源Mediapipe人工智能算法库,识别人体姿态,来判断跳绳次数,并通过Pinpong库控制LED灯实时显示次数。
【测试程序】
测试程序中,使用人体姿态23,24两坐标点中点与标准点的比较来确认跳绳完成程度。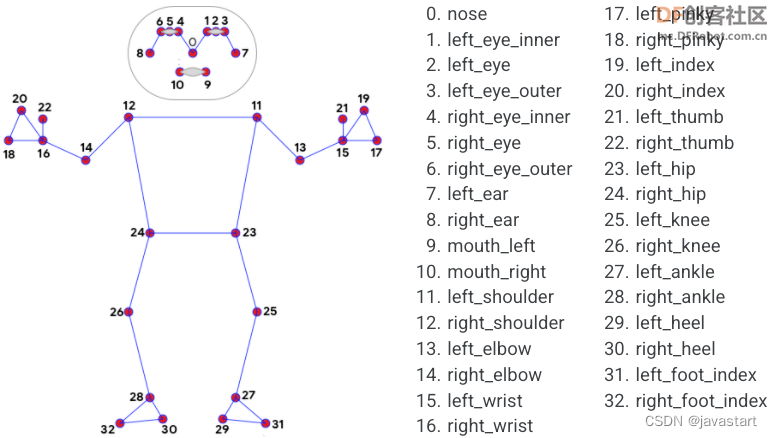
import numpy as np import time import cv2 import PoseModule as pm cap = cv2.VideoCapture("tiaosheng.mp4") detector = pm.poseDetector() count = 0 dir = 0 pTime = 0 success=True point_sd=0 while success: success, img = cap.read() if success: img = cv2.resize(img, (640, 480)) img = detector.findPose(img, False) lmList = detector.findPosition(img, False) if len(lmList) != 0: point = detector.midpoint(img, 24, 23) if point_sd==0: point_sd=point print(point_sd["y"]) # 计算个数 print(point["y"]) if point["y"]> point_sd["y"]+15: if dir == 0: count += 0.5 dir = 1 if point["y"]<point_sd["y"]+5: if dir == 1: count += 0.5 dir = 0 #print(count) cv2.putText(img, str(int(count)), (45, 460), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 7,(255, 0, 0), 8) cTime = time.time() fps = 1 / (cTime - pTime) pTime = cTime cv2.putText(img, str(int(fps)), (50, 100), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 5,(255, 0, 0), 5) cv2.imshow("Image", img) cv2.waitKey(1)
复制代码
【PoseModule.py】
上面程序用到的“PoseModule.py”文件中,在”poseDetector“类中增加了“midpoint”函数,用于求两点的中点坐标。
import math import mediapipe as mp import cv2 class poseDetector(): def __init__(self, mode=False, upBody=False, smooth=True, detectionCon=0.5, trackCon=0.5): self.mode = mode self.upBody = upBody self.smooth = smooth self.detectionCon = detectionCon self.trackCon = trackCon self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils self.mpPose = mp.solutions.pose self.pose = self.mpPose.Pose(self.mode, self.upBody, self.smooth, self.detectionCon, self.trackCon) def findPose(self, img, draw=True): imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) self.results = self.pose.process(imgRGB) if self.results.pose_landmarks: if draw: self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, self.results.pose_landmarks, self.mpPose.POSE_CONNECTIONS) return img def findPosition(self, img, draw=True): self.lmList = [] if self.results.pose_landmarks: for id, lm in enumerate(self.results.pose_landmarks.landmark): h, w, c = img.shape # print(id, lm) cx, cy = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h) self.lmList.append([id, cx, cy]) if draw: cv2.circle(img, (cx, cy), 5, (255, 0, 0), cv2.FILLED) return self.lmList def midpoint(self,img,p1,p2,draw=True): x1, y1 = self.lmList[p1][1:] x2, y2 = self.lmList[p2][1:] x3=int((x1+x2)/2) y3=int((y1+y2)/2) if draw: cv2.circle(img, (x3, y3), 10, (0, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) cv2.circle(img, (x3, y3), 15, (0, 0, 255), 2) point={"x":x3,"y":y3} return point def findAngle(self, img, p1, p2, p3, draw=True): # Get the landmarks x1, y1 = self.lmList[p1][1:] x2, y2 = self.lmList[p2][1:] x3, y3 = self.lmList[p3][1:] # Calculate the Angle angle = math.degrees(math.atan2(y3 - y2, x3 - x2) - math.atan2(y1 - y2, x1 - x2)) if angle < 0: angle += 360 # print(angle) # Draw if draw: cv2.line(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (255, 255, 255), 3) cv2.line(img, (x3, y3), (x2, y2), (255, 255, 255), 3) cv2.circle(img, (x1, y1), 10, (0, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) cv2.circle(img, (x1, y1), 15, (0, 0, 255), 2) cv2.circle(img, (x2, y2), 10, (0, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) cv2.circle(img, (x2, y2), 15, (0, 0, 255), 2) cv2.circle(img, (x3, y3), 10, (0, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) cv2.circle(img, (x3, y3), 15, (0, 0, 255), 2) cv2.putText(img, str(int(angle)), (x2 - 50, y2 + 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 2, (0, 0, 255), 2) return angle
复制代码
【测试网络视频】
【存在的问题】
测试结果令人比较满意,但这里存在这样两个问题:1、标准点point_sd这个坐标是以视频开始第一帧画面是站在原地未起跳为前提。
2、标准点纵坐标的判定区间(point_sd["y"]+5与 point_sd["y"]+15)是根据运行后的数据人为分析出来的,只对这一段视频有效,不具有通用性。
【解决问题思路】
1、在正式跳绳计数前,先试跳,通过数据分析出标准点、判定区间(防止数据在判定点抖动,出现错误计数)。在上个程序中判定点为:point_sd["y"]+10。
2、以手势控制屏幕上的虚拟按钮来分析初始化数据,并启动跳绳计数及终止计数。
【解决问题步骤】
第一步:实现手势控制屏幕按钮。
程序中使用了计时器,以防止连续触发问题。
import cv2 import numpy as np import time import os import HandTrackingModule as htm ####################### brushThickness = 25 eraserThickness = 100 ######################## drawColor = (255, 0, 255) cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) cap.set(3, 640) cap.set(4, 480) detector = htm.handDetector(detectionCon=0.65,maxHands=1) imgCanvas = np.zeros((480, 640, 3), np.uint8) rect=[(20, 20), (120, 120)] font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX cv2.rectangle(imgCanvas, rect[0], rect[1],(0, 255, 0), 2) cv2.putText(imgCanvas, "SET", (45,85), font, 1, drawColor, 2) bs=0 bs2=0 while True: # 1. Import image success, img = cap.read() if success: img = cv2.flip(img, 1) # 2. Find Hand Landmarks img = detector.findHands(img) lmList = detector.findPosition(img, draw=False) if len(lmList) !=0: # tip of index and middle fingers x1, y1 = lmList[8][1:] x2, y2 = lmList[12][1:] # 3. Check which fingers are up fingers = detector.fingersUp() # print(fingers) # 5. Index finger is up if fingers[1] and fingers[2] == False: cv2.circle(img, (x1, y1), 15, drawColor, cv2.FILLED) if bs2==1: if time.time()-time_start>3: bs2=0 else: if x1>rect[0][0] and x1<rect[1][0] and y1>rect[0][1] and y1<rect[1][1]: if bs==0: print("OK") imgCanvas = np.zeros((480, 640, 3), np.uint8) cv2.rectangle(imgCanvas, rect[0], rect[1],(0, 255, 0), 2) cv2.putText(imgCanvas, "STOP", (30,85), font, 1, drawColor, 2) bs=1 bs2=1 time_start=time.time() else: imgCanvas = np.zeros((480, 640, 3), np.uint8) imgGray = cv2.cvtColor(imgCanvas, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) img = cv2.bitwise_or(img,imgCanvas) # img = cv2.addWeighted(img,0.5,imgCanvas,0.5,0) cv2.imshow("Image", img) cv2.waitKey(1)
复制代码
上面程序引用的“HandTrackingModule.py”文件。
import cv2 import mediapipe as mp import time import math import numpy as np class handDetector(): def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=2, detectionCon=0.8, trackCon=0.5): self.mode = mode self.maxHands = maxHands self.detectionCon = detectionCon self.trackCon = trackCon self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands(self.mode, self.maxHands, self.detectionCon, self.trackCon) self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils self.tipIds = [4, 8, 12, 16, 20] def findHands(self, img, draw=True): imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB) # print(results.multi_hand_landmarks) if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if draw: self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms, self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS) return img def findPosition(self, img, handNo=0, draw=True): xList = [] yList = [] bbox = [] self.lmList = [] if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo] for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark): # print(id, lm) h, w, c = img.shape cx, cy = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h) xList.append(cx) yList.append(cy) # print(id, cx, cy) self.lmList.append([id, cx, cy]) if draw: cv2.circle(img, (cx, cy), 5, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) xmin, xmax = min(xList), max(xList) ymin, ymax = min(yList), max(yList) bbox = xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax if draw: cv2.rectangle(img, (xmin - 20, ymin - 20), (xmax + 20, ymax + 20), (0, 255, 0), 2) return self.lmList def fingersUp(self): fingers = [] # Thumb if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][1] > self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][1]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) # Fingers for id in range(1, 5): if self.lmList[self.tipIds[id]][2] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[id] - 2][2]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) # totalFingers = fingers.count(1) return fingers def findDistance(self, p1, p2, img, draw=True,r=15, t=3): x1, y1 = self.lmList[p1][1:] x2, y2 = self.lmList[p2][1:] cx, cy = (x1 + x2) // 2, (y1 + y2) // 2 if draw: cv2.line(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (255, 0, 255), t) cv2.circle(img, (x1, y1), r, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) cv2.circle(img, (x2, y2), r, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) cv2.circle(img, (cx, cy), r, (0, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) length = math.hypot(x2 - x1, y2 - y1) return length, img, [x1, y1, x2, y2, cx, cy]
复制代码第二步,分析数据,得到判定点纵坐标。思路是,坐标数据是上下波动,将数据中的波峰和波谷分别提取出来计算均值,然后取中值,和差值。中值为判定点,差值用来确定判定区域。波峰和波谷的判定采用的是两边数据与当前数据做差值看差值方向,如果方向相反,即为峰值。但这里就存在,Mediapipe识别准确度的问题,可能在上升或下降的过程中数据不平滑,出现数据波动。可能在分析时,出现误判,采集到错误的峰值。后期可采用滤波算法处理此问题。现在看效果,还不错。
import numpy as np import time import cv2 import PoseModule as pm import math def max_min(a): h = [] l = [] for i in range(1, len(a)-1): if(a[i-1] < a[i] and a[i+1] < a[i]): h.append(a[i]) elif(a[i-1] > a[i] and a[i+1] > a[i]): l.append(a[i]) if(len(h) == 0): h.append(max(a)) if(len(l) == 0): l.append(min(a[a.index(max(a)):])) mid=(np.mean(h)+np.mean(l))/2 print(int(mid),int(np.mean(h)-np.mean(l))) return(int(mid),int(np.mean(h)-np.mean(l))) cap = cv2.VideoCapture("tiaosheng.mp4") detector = pm.poseDetector() count = 0 dir = 0 pTime = 0 success=True point=[] while success: success, img = cap.read() if success: img = cv2.resize(img, (640, 480)) img = detector.findPose(img, False) lmList = detector.findPosition(img, False) if len(lmList) != 0: point_tem=detector.midpoint(img, 24, 23) point.append(point_tem['y']) cv2.putText(img, str(point_tem['y']), (45, 460), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 7,(255, 0, 0), 8) cTime = time.time() fps = 1 / (cTime - pTime) pTime = cTime cv2.putText(img, str(int(fps)), (50, 100), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 5,(255, 0, 0), 5) cv2.imshow("Image", img) cv2.waitKey(1) max_min(point) cap.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows()
复制代码
最终得到“304 26”为“中值 差值” 【完整程序】
将以上分段程序进行整合,得到完整程序,并进行实地测试。(纯手工敲码)
import cv2 import numpy as np import time import os import HandTrackingModule as htm import PoseModule as pm #计算判定点 def max_min(a): h = [] l = [] for i in range(1, len(a)-1): if(a[i-1] < a[i] and a[i+1] < a[i]): h.append(a[i]) elif(a[i-1] > a[i] and a[i+1] > a[i]): l.append(a[i]) if(len(h) == 0): h.append(max(a)) if(len(l) == 0): l.append(min(a[a.index(max(a)):])) mid=(np.mean(h)+np.mean(l))/2 print(int(mid),int(np.mean(h)-np.mean(l))) return(int(mid),int(np.mean(h)-np.mean(l))) ####################### brushThickness = 25 eraserThickness = 100 ######################## drawColor = (255, 0, 255) cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) cap.set(3, 640) cap.set(4, 480) detector_hand = htm.handDetector(detectionCon=0.65,maxHands=1) detector_pose = pm.poseDetector() imgCanvas = np.zeros((480, 640, 3), np.uint8) rect=[(20, 20), (120, 120)] font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX cv2.rectangle(imgCanvas, rect[0], rect[1],(0, 255, 0), 2) cv2.putText(imgCanvas, "SET", (45,85), font, 1, drawColor, 2) bs=0 bs2=0 bs3=0 point=[] count=0 pTime = 0 dire=0 while True: success, img = cap.read() if success: img = cv2.flip(img, 1) if bs==1 and bs2==0: if bs3==1: if time.time()-time_start<4: cv2.putText(img, str(3-int(time.time()-time_start)), (300, 240), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 10,(255, 255, 0), 5) else: bs3=0 time_start=time.time() else: if time.time()-time_start<11: img = detector_pose.findPose(img, False) lmList = detector_pose.findPosition(img, False) if len(lmList) != 0: point_tem=detector_pose.midpoint(img, 24, 23) point.append(point_tem['y']) cv2.putText(img, str(point_tem['y']), (45, 460), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 7,(255, 0, 0), 8) cv2.putText(img, str(10-int(time.time()-time_start)), (500, 460), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 10,(255, 255, 0), 5) else: point_sd,l=max_min(point) bs=2 cv2.rectangle(imgCanvas, rect[0], rect[1],(0, 255, 0), 2) cv2.putText(imgCanvas, "START", (30,85), font, 1, drawColor, 2) if bs==3 and bs2==0: if bs3==1: if time.time()-time_start<4: cv2.putText(img, str(3-int(time.time()-time_start)), (300, 240), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 10,(255, 255, 0), 5) else: bs3=0 time_start=time.time() else: img = detector_pose.findPose(img, False) lmList = detector_pose.findPosition(img, False) if len(lmList) != 0: point = detector_pose.midpoint(img, 24, 23) if point["y"]> point_sd+l/4: if dire == 0: count += 0.5 dire = 1 if point["y"]<point_sd-l/4: if dire == 1: count += 0.5 dire = 0 cv2.putText(img, str(int(count)), (45, 460), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 7,(255, 0, 0), 8) if bs2==1:#等待三秒 if time.time()-time_start>4: bs2=0 time_start=time.time() else: #手势操作 img = detector_hand.findHands(img) lmList = detector_hand.findPosition(img, draw=False) if len(lmList) !=0: x1, y1 = lmList[8][1:] x2, y2 = lmList[12][1:] fingers = detector_hand.fingersUp() #出示食指 if fingers[1] and fingers[2] == False: cv2.circle(img, (x1, y1), 15, drawColor, cv2.FILLED) if x1>rect[0][0] and x1<rect[1][0] and y1>rect[0][1] and y1<rect[1][1]:#食指进入按钮区域 if bs==0: print("OK") imgCanvas = np.zeros((480, 640, 3), np.uint8) bs=1 bs2=1 bs3=1 time_start=time.time() elif bs==1: imgCanvas = np.zeros((480, 640, 3), np.uint8) bs2=1 bs3=1 time_start=time.time() elif bs==2: imgCanvas = np.zeros((480, 640, 3), np.uint8) cv2.rectangle(imgCanvas, rect[0], rect[1],(0, 255, 0), 2) cv2.putText(imgCanvas, "STOP", (30,85), font, 1, drawColor, 2) bs=3 bs2=1 bs3=1 time_start=time.time() elif bs==3: imgCanvas = np.zeros((480, 640, 3), np.uint8) cv2.rectangle(imgCanvas, rect[0], rect[1],(0, 255, 0), 2) cv2.putText(imgCanvas, "START", (30,85), font, 1, drawColor, 2) bs=2 bs2=1 bs3=1 time_start=time.time() cTime = time.time() fps = 1 / (cTime - pTime) pTime = cTime cv2.putText(img, str(int(fps)), (500, 100), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 5,(255, 0, 0), 5) imgGray = cv2.cvtColor(imgCanvas, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) img = cv2.bitwise_or(img,imgCanvas) cv2.imshow("Image", img) cv2.waitKey(1)
复制代码
【计数炫灯】
使用Pinpong库,连接Micro:bit,控制LED灯随跳绳次数增加亮灯数。
|


