怎么在自己的电脑上做网站泉州网站建设方案维护
一 概述
最近遇到一个问题,linux 的 smb服务器开启匿名访问,windows访问linux文件夹不需要用户名密码就可以进去使用,但是存在一个问题,ssh连接到linux 后修改的文件,在windows已smb方式下打开某个文件修改 是没有权限的,所以需要 windows用ssh登录linux相同的用户名 登录smb服务器,那样才能已同样的权限控制。进行以下几步即可
1. 打开 映射网络 驱动器,
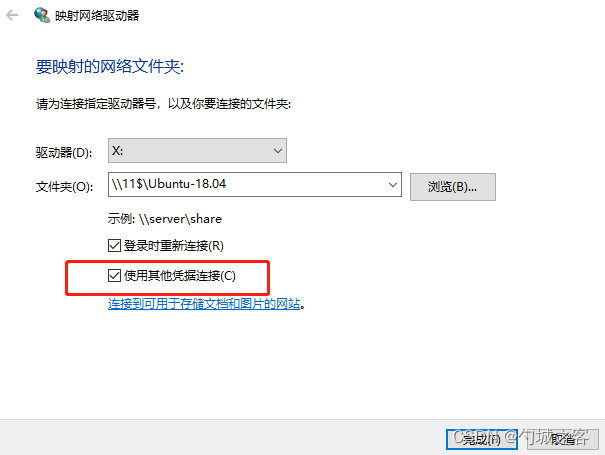
把图片中红色 打勾,点击 “完成” 就会弹出对应框让你输入 新的用户名密码 登录
二 ubunut上安装smb服务器
1.安装samba
sudo apt-get install samba smbfs -y
2.配置共享文件夹
备份并编辑smb.conf允许网络用户访问
sudo cp /etc/samba/smb .conf /etc/samba/smb .conf_backup
sudo vim /etc/samba/smb .conf
增加内容如下
[Share]
comment = Shared Folder for debug in remote win client
netbios name=smb_test_server
path= /opt/smbkiki
valid users =smbkiki
create mask=0644
directory mask=0755
force user=zlgci
force group=root
public= yes
writable= yes
browseable= yes
available= yes
说明
- netbios name 在windows 网上领居 能够看到的名字
- path 要共享的目录
- valid users 能够访问该共享的用户,可用通配符
- create mask 和 directory mask 表示新建文件 目录时的权限
- force user 和 force group 表示进行读写时映射到服务器端对应的用户和用户组
- writable 表示可写
- browseable表示可以浏览。
- 找到[global]把 workgroup = MSHOME 改成workgroup = WORKGROUP
就是改为跟你的win在同一个工作组
3. 添加SMB客户端访问的账号(例如用户名为:smbkiki)
- 如果ubuntu系统还没这个账户则先添加
sudo useradd smbkiki
- 将smbkiki添加到smb访问账户名单里,并设置密码
sudo smbpasswd -a smbkiki
4.重启smb服务器
sudo /etc/init.d/smbd restart
5.windows上访问smb服务器
快捷键 win+r ,输入 \IP地址 即可访问,如果要指定用户名来映射网络驱动器,请看文章开头的部分。
