门户网站建设方案目录网页升级未成年人自行离开

💻文章目录
- 📄前言
- 红黑树
- 概念
- 红黑树的结构
- 红黑树节点的定义
- 红黑树的定义
- 红黑树的调整
- 红黑树的迭代器
- 迭代器的声明
- operator( )++
- opeartor--( )
- 完整代码
- 📓总结
📄前言
作为一名程序员相信你一定有所听闻红黑树的大名,像是手撕红黑树这样的名梗已经几乎传遍了程序员之间,如果你还不会“手撕”红黑树,那么本文将会教会你如何“手撕”红黑树。
红黑树
概念
红黑树,顾名思义是只有红色和黑色两种颜色的树,由 Rudolf Bayer 在1972年发明的。红黑树是一种高效的查找树,可以在 O ( l o g 2 n ) O(log_2n) O(log2n)的时间复杂度下进行查找、插入和删除,C++中的map和set的底层也是利用红黑树所构成,在深入学习红黑树前,先让我们学习一下它的特性吧。
红黑树的特性:
- 根节点为黑
t2. 最长路径的长度不超过最短路径的长度的两倍 - 每条路径的黑色节点之和都相同
- 不能存在连续的红色节点
- 只存在红色或黑色的节点
- 中序遍历是有序的
红黑树的样例:
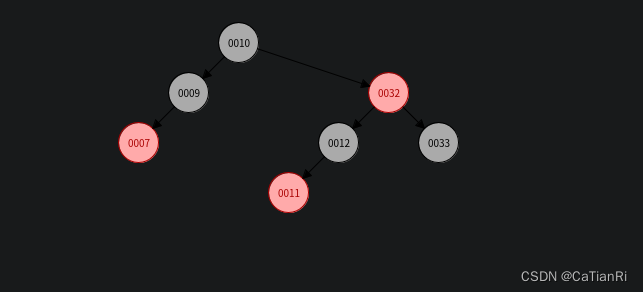

从图例我们可以看出每条路径的黑色节点个数都是相同的并且没有连续的红色节点,只要满足这两条特性,红黑树的最长路径节点个数不会超过最短节点个数的两倍,从而维护了树的平衡。
红黑树的结构
红黑树节点的定义
在进入插入操作前,得先定义好树的节点。因为树的插入需要用到父节点、甚至祖父节点,所以为了方便插入,二叉树的节点新增了父节点的指针。
enum Color //颜色的定义
{RED, //0BLACK //1
};template <class _Value>
struct RBTreeNode //红黑树节点的定义
{RBTreeNode<_Value>* _left; //节点的左孩子RBTreeNode<_Value>* _right; //节点的右孩子RBTreeNode<_Value>* _parent; //节点的双亲Color _col; //节点的颜色_Value _data; //节点的数值RBTreeNode(const _Value& data = _Value()) //节点的构造函数:_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr),_data(data),_col(RED) //默认设节点为红色{}
};
红黑树的定义
C++的红黑树在实现上为了同时让map和set复用,增加了一个keyofvalue的模板参数,用来解析需要比较的数值,如果不打算实现set和map可以不用写。
template<class _Key, class _Value, class _KeyOfValue>
/*如果愿意还可以加上一个compare参数,来比较数值*/
class RBTree
{
public:typedef RBTreeNode<_Value> Node;/*这里暂时先把insert的返回值设为Node*,迭代器后面介绍时再补充*/Node* insert(const _Value data) {if(_root == nullptr) //节点为空则新建{_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK; //红黑书性质规定根节点必须为黑return _root;}_KeyOfValue kot; //用来解析数据的伪函数Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr; while(cur) /*二叉树搜索树的经典搜索过程*/{//工作原理:是data是pair类型则返回data.first,正常内置类型直接返回dataif(kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)) { parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if(kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else return cur;}cur = new Node(data);Node* ret = cur;cur->_parent = parent; /*链接父节点*//*父节点链接子节点*/if(kot(cur->_data) < kot(parent->_data))parent->_left = cur;else parent->_right = cur; /***************检查红黑树是否违反性质**************/}
}
红黑树的调整
红黑树的每次插入都需要检查其性质是否遭到了破坏,因为节点默认颜色为红色,所以当父节点为黑色时,则不需要调整。如果父节点为红色,违反了红黑树的性质,根据红黑树的情况,共有六种情况需要讨论,其中需要利用到祖父节点,根据父节点在祖父节点的左孩子/右孩子,又将6种情况划分为两类。
为了方便讨论,这里把当前节点作为cur,cur的父节点为p,cur的祖父节点为g,p的兄弟节点为u
-
父节点是祖父节点的左孩子
-
情况一:cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u存在且为红
这种情况下,需要把p节点和u节点设为黑色,如果g节点为根节点则退出调整,否则将g节点设为红色,并把g赋值给cur,继续向上调整。
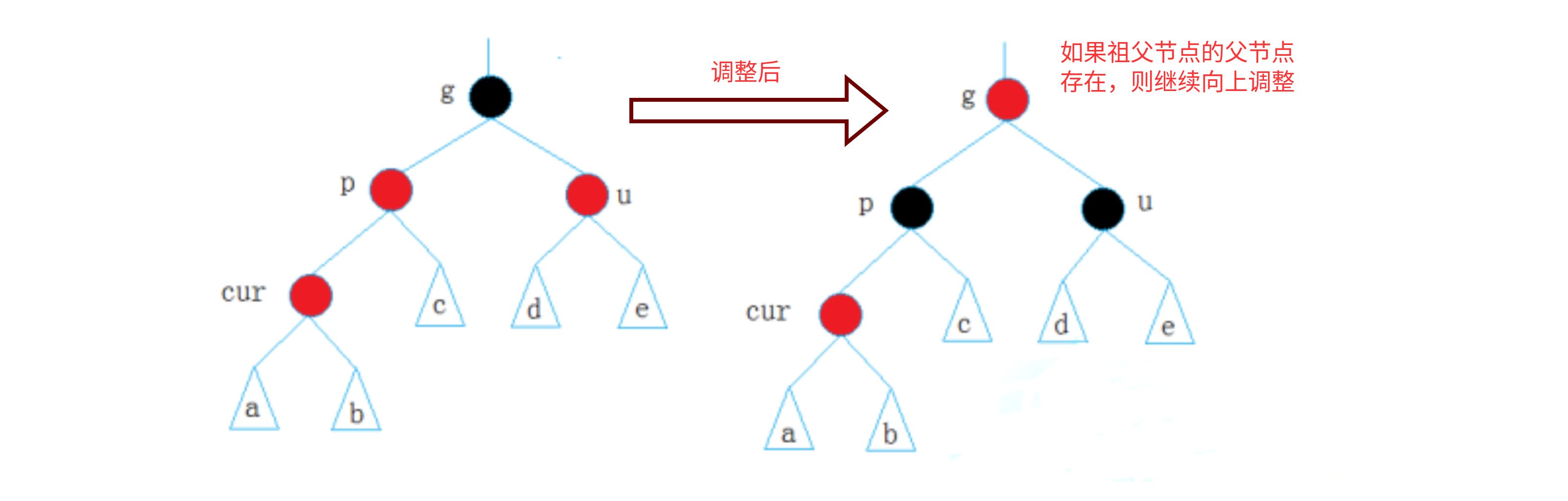
if(uncle && uncle->_col == RED) {parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandParent->_col = RED;cur = grandParent;parent = cur->_parent; } -
情况二:cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/存在且为黑,并且cur为p的左孩子
这种情况下,需要对p节点进行右旋操作,并将p节点改为黑,cur和g节点改为红。
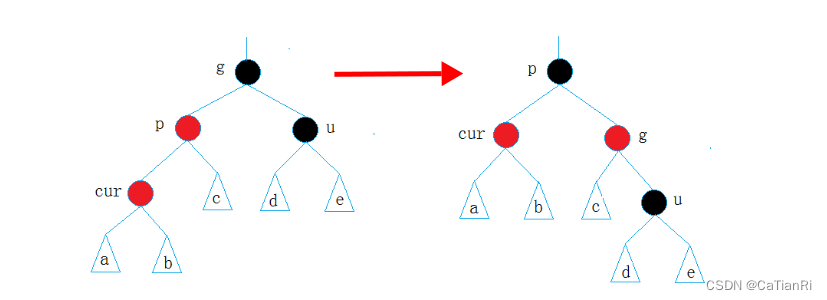
if(uncle && uncle->_col == BLACK) {parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandParent->_col = RED;cur = grandParent;parent = cur->_parent; } -
情况三:cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/存在且为黑,并且cur为p的左孩子
在这种情况下,需要对双旋操作,先对p节点进行左旋,使得树变得极端左倾,然后再对g节点进行右倾恢复平衡,最后将g改为红,p改为黑。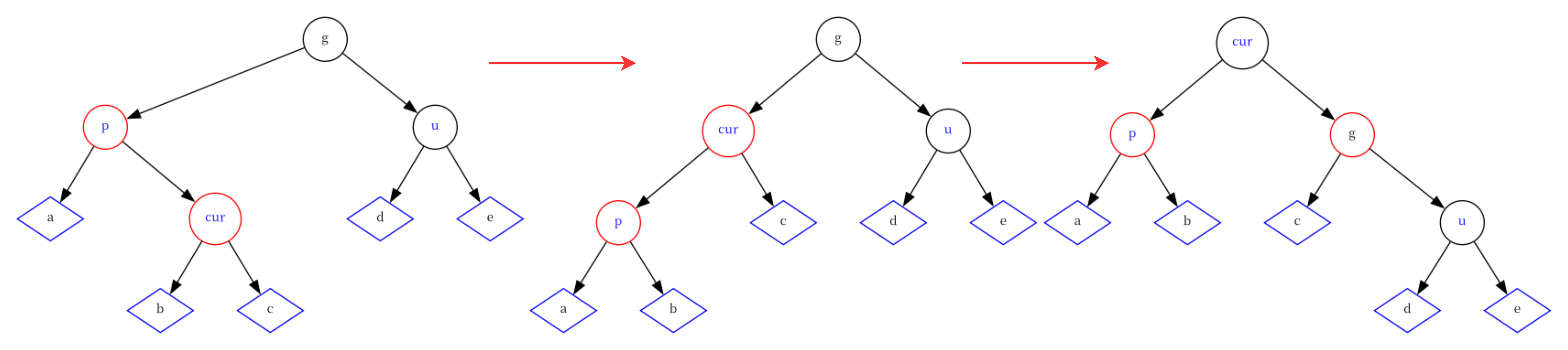
else {RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandParent);grandParent->_col = RED;cur->_col = BLACK; }
-
-
父节点是祖父节点的右孩子
-
情况四:cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u存在且为红
与情况一的处理一样
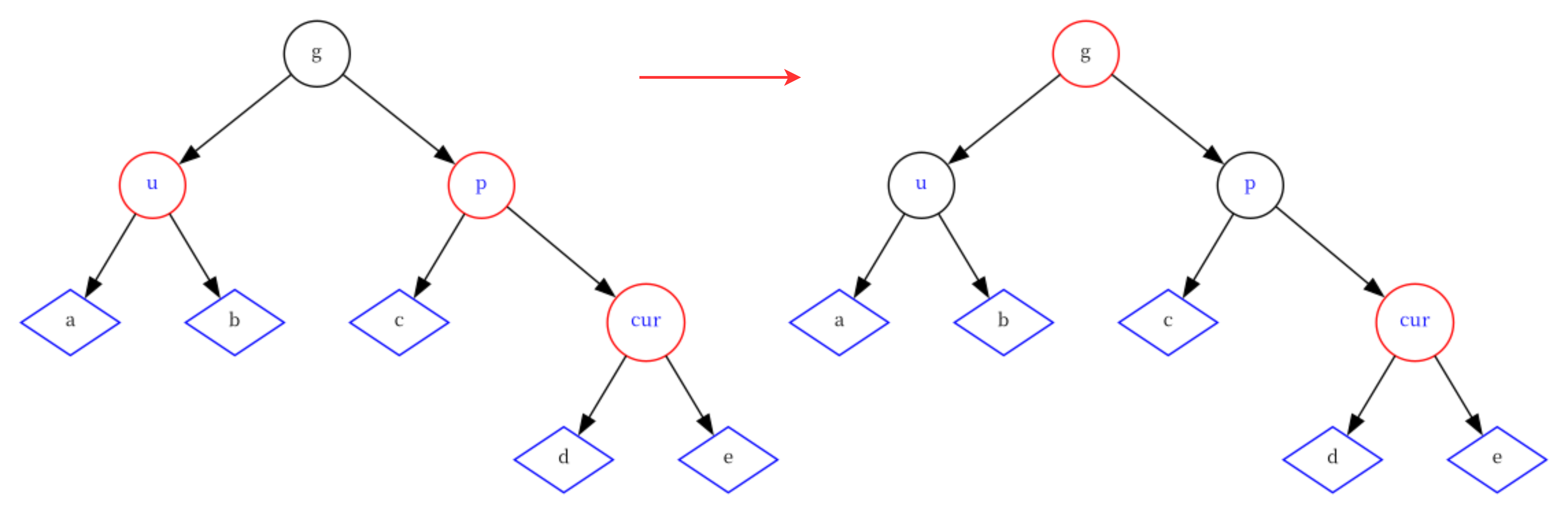
if(uncle && uncle->_col == BLACK) {parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandParent->_col = RED;cur = grandParent;parent = cur->_parent; } -
情况五:cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/存在且为黑, 并且cur为p的左孩子
这种情况下,需要对g节点进行左旋操作,并把p节点改黑、g节点改红。
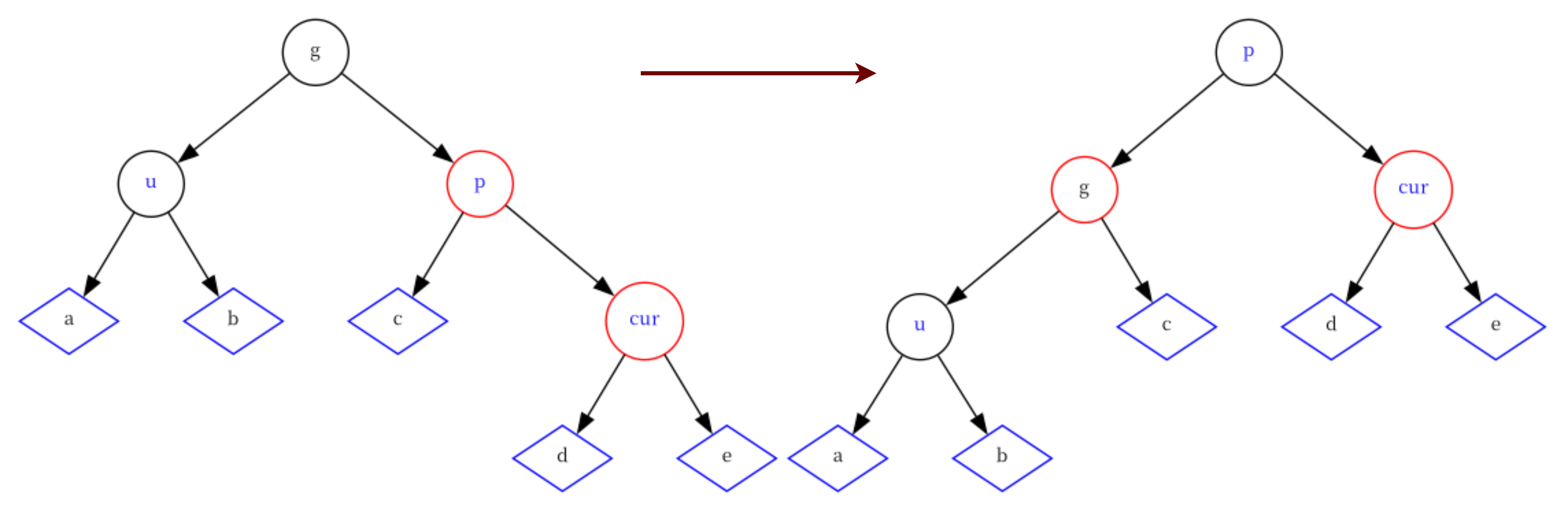
if(cur == parent->_right) {RotateL(grandParent);parent->_col = BLACK;grandParent->_col = RED; } -
情况六:cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/存在且为黑, 并且cur为p的右孩子
这种情况下,需要对p节点进行右旋,使树变得极端右倾,然后对g节点进行左旋,最后将g节点改红、cur节点改黑。
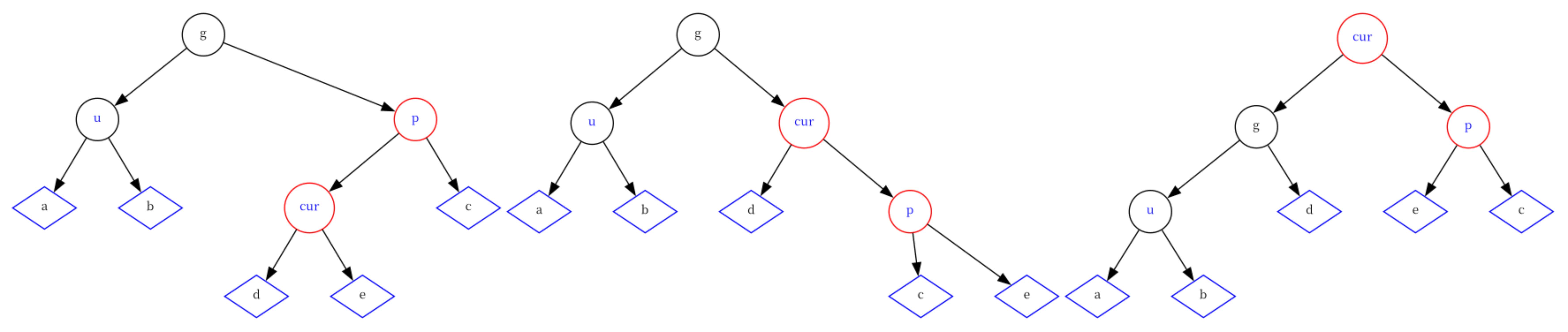
else {RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandParent);grandParent->_col = RED;cur->_col = BLACK; } -
红黑树的迭代器
做完了树的插入,接下来就是红黑树的迭代器了。因为红黑树是平衡树,所以它的最小节点在树的最左侧,最大节点在树的最右侧,为此我们可以使用一个头节点,让其左右孩子指向最大最小节点,父节点指向跟节点。
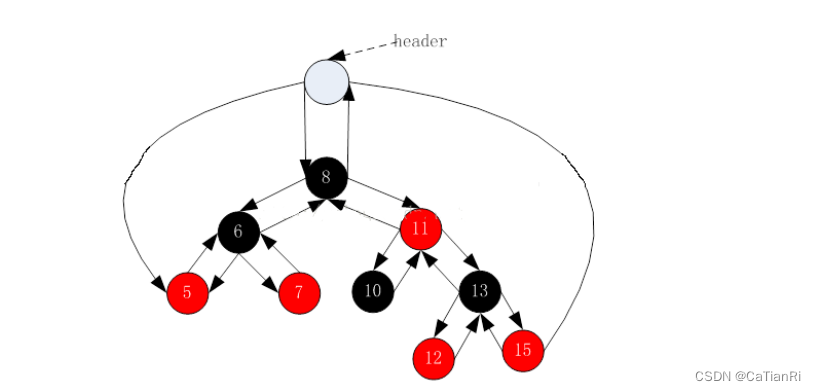
迭代器的声明
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr> //Ref、Ptr用于const_iterator
struct _TreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef _TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;Node* _node;self& operator--();self& operator++();
}
operator( )++
找平衡树的下一个比当前节点大的节点,有两种情况
- 当前节点存在右节点,则找右节点最左边的节点。
- 不存在右节点,则返回父节点直到当前节点不是父节点的左节点
self& operator++() /*寻找下一个更大节点*/
{if(_node->_right) {Node* cur = _node->_right;while(cur->_left) /*寻找最左侧节点*/cur = cur->_left;_node = cur;}else {Node* cur = _node; Node* parent = cur->_parent; while(parent && cur == parent->_right){ /*右子树不存在,继续向上调整*/cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;
}
opeartor–( )
寻找上一节点也分两种情况。
- 当前节点左孩子存在,则找到左孩子的最右侧节点。
- 当前节点不存在左孩子,则向上寻找直到当前节点不再是父节点的左孩子
self& operator--()
{Node* cur = _node;if(cur->_col == RED && cur->_parent->_parent == cur){ //当前节点为头节点cur = cur->_right;}if(cur->_left){ //左子树存在,在左子树寻找最大节点cur = cur->_left;while(cur->_right)cur = cur->_right;}else{ //向上调整Node* parent = cur->_parent;while(parent && cur == parent->_left){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}cur = parent;}_node = cur;return *this;
}
完整代码
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct _TreeIterator //迭代器
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef _TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;typedef _TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator; Node* _node;_TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}_TreeIterator(const iterator& _it) //构造函数,方便以后实现set中的inset函数中的pair拷贝:_node(_it._node){}Ref operator*()const{return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->()const{return &operator*();}self& operator--(){Node* cur = _node;if(cur->_col == RED && cur->_parent->_parent == cur){ cur = cur->_right;}if(cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;while(cur->_right)cur = cur->_right;}else{Node* parent = cur->_parent;while(parent && cur == parent->_left){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}cur = parent;}_node = cur;return *this;}self&& operator--(int){self tem = *this;Node* cur = _node;if(cur->_col == RED && cur->_parent->_parent == cur){cur = cur->_right;}if(cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;while(cur->_right)cur = cur->_right;}else{Node* parent = cur->_parent;while(parent && cur == parent->_left){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}cur = parent;}_node = cur;return tem;}self& operator++(){if(_node->_right){Node* cur = _node->_right;while(cur->_left)cur = cur->_left;_node = cur;}else {Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while(parent && cur == parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}bool operator!=(const self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const self& s){return _node == s._node;}
};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT> //可是选择加上 class compare
class RBTree
{
public:typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef _TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef _TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator; RBTree(){ //提前开好头节点_root = new Node;_root->_left = _root;_root->_right = _root;}const_iterator begin() const {return const_iterator(LeftMost());}const_iterator end() const {return const_iterator(_root);}iterator begin(){return iterator(LeftMost());}iterator end(){return iterator(_root);}std::pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data); //上文insert返回值设为了Node*,但实际应该是这个// 检测红黑树中是否存在值为data的节点,存在返回该节点的地址,否则返回nullptriterator Find(const K& data);const_iterator Find(const K& data) const;// 获取红黑树最左侧节点Node* LeftMost()const;// 中序遍历void InOrder() {_InOrder(GetRoot());std::cout << std::endl;}// 获取红黑树最右侧节点Node* RightMost()const;// 检测红黑树是否为有效的红黑树,注意:其内部主要依靠_IsValidRBTRee函数检测bool IsValidRBTRee();
private:bool _IsValidRBTRee(Node* pRoot, size_t blackCount, const size_t pathBlack);// 左单旋void RotateL(Node* pParent);// 右单旋void RotateR(Node* pParent);// 为了操作树简单起见:获取根节点Node*& GetRoot() const { return _root->_parent; }void _InOrder(Node* root);void rebalance(Node*& cur, Node*& parent) //红黑树的平衡调整{while (parent != _root && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandParent = parent->_parent;if(parent == grandParent->_left){Node* uncle = grandParent->_right;if(uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandParent->_col = RED;cur = grandParent;parent = cur->_parent;}else {if(cur == parent->_left){ //右旋RotateR(grandParent);parent->_col = BLACK;grandParent->_col = RED;}else { //双旋RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandParent);grandParent->_col = RED;cur->_col = BLACK;}break;}}else {Node* uncle = grandParent->_left;if(uncle && uncle->_col == BLACK){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandParent->_col = RED;cur = grandParent;parent = cur->_parent;}else {if(cur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandParent);parent->_col = BLACK;grandParent->_col = RED;}else {RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandParent);grandParent->_col = RED;cur->_col = BLACK;}break;}}}GetRoot()->_col = BLACK;}
private:Node* _root = nullptr;KeyOfT kot;
};template <class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
typename RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>::const_iterator RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>::Find(const K& data) const
{Node* cur = GetRoot();while(cur){if(kot(cur->_data) < data){cur = cur->_right;}else if(kot(cur->_data) > data){cur = cur->_left;}else {return cur;}}return nullptr;
}template <class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
typename RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>::iterator RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>::Find(const K& data)
{Node* cur = GetRoot();while(cur){if(kot(cur->_data) < data){cur = cur->_right;}else if(kot(cur->_data) > data){cur = cur->_left;}else {return cur;}}return nullptr;
}template <class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
void RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>::_InOrder(Node* root) //中序遍历
{if(!root) return;_InOrder(root->_left);std::cout << root->_data << " ";_InOrder(root->_right);
}template <class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
typename RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>::Node* RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>::LeftMost()const //最左节点
{return _root->_left;
}template <class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
typename RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>::Node* RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>::RightMost()const //最右节点
{return _root->_right;
}template <class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
bool RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>::IsValidRBTRee() //检查树的性质是否被破坏
{if(!GetRoot() || GetRoot()->_col == RED) return false;size_t pathBlack = 0;Node* cur = GetRoot();while(cur){if(cur->_col == BLACK)++pathBlack; //计算路径黑色节点的总个数cur = cur->_left;}int blackCount = 0;return _IsValidRBTRee(GetRoot(), blackCount, pathBlack);
}template <class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
bool RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>::_IsValidRBTRee(Node* pRoot, size_t blackCount, const size_t pathBlack)
{if(!pRoot){if(blackCount != pathBlack){std::cout << "有连续的红色结点" << std::endl;return false;}return true;}if(pRoot->_col == RED && pRoot->_parent->_col == RED){std::cout << "有连续的红色结点" << std::endl;return false;}if(pRoot->_col == BLACK)++blackCount;return _IsValidRBTRee(pRoot->_left, blackCount, pathBlack)&& _IsValidRBTRee(pRoot->_right, blackCount, pathBlack);
}template <class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
std::pair<typename RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>::iterator, bool> RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>::Insert(const T& data)
{if(GetRoot() == nullptr){Node* node = new Node(data);node->_col = BLACK;node->_parent = _root;_root->_parent = node;_root->_left = _root->_parent;_root->_right = _root->_parent;return std::make_pair(iterator(GetRoot()), true);}Node* cur = GetRoot();Node* parent = nullptr;while(cur){if(kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if(kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else return std::make_pair(iterator(cur), false);}cur = new Node(data);Node* ret = cur; //记录新增的节点,因为在调整后,节点可能会丢失cur->_parent = parent;if(kot(cur->_data) < kot(parent->_data)){if (parent == _root->_left) //更新最小节点_root->_left = cur;parent->_left = cur;}else {if(parent == _root->_right) //更新最大节点_root->_right = cur;parent->_right = cur;}rebalance(cur, parent);return std::make_pair(ret, true);
}template <class K, class V, class KeyOfT>
void RBTree<K, V, KeyOfT>::RotateL(Node* parent) //左旋
{Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;parent->_right = subRL;parent->_parent = subR;subR->_parent = parentParent;subR->_left = parent;if(subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;if(GetRoot() == parent){GetRoot() = subR;}else {if(parent == parentParent->_left){parentParent->_left = subR;}else {parentParent->_right = subR;}}
}template <class K, class V, class KeyOfT>
void RBTree<K, V, KeyOfT>::RotateR(Node* parent) //右旋
{Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;subL->_parent = parentParent;parent->_left = subLR;parent->_parent = subL;if(subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;if(parent == GetRoot())GetRoot() = subL;else{if(parent == parentParent->_left)parentParent->_left = subL;elseparentParent->_right = subL;}
}
📓总结
📜博客主页:主页
📫我的专栏:C++
📱我的github:github

