惠安网站建设价格天津网站开发贴吧

Part.1 行业背景
三维视觉引导技术在国内外汽车零部件领域得到了广泛应用。随着汽车制造业的不断发展和创新,对于零部件的加工和装配要求越来越高,而三维视觉引导技术能够帮助企业实现更精确、更高效的零部件上下料过程。
纵览国外,部分汽车零部件制造商已经将三维视觉引导技术应用于汽车零部件的加工和装配过程中。例如,德国的汽车零部件制造商 Bosch、ZF、Audi 等都采用了三维视觉引导技术来提高零部件的加工精度和装配质量。
国内情况来看,三维视觉引导技术在汽车零部件领域也得到了广泛应用。以奇瑞汽车、吉利汽车、长城汽车等国内汽车企业为例,他们都采用了三维视觉引导技术来实现汽车零部件的自动装配和上下料。除汽车企业外,一些国内的高科技企业,如阿里巴巴、华为等,也将其应用于汽车零部件的制造和装配过程中。
总的来说,三维视觉引导技术在国内外汽车零部件领域中具有广泛的应用前景。把工业机器人、数控机床、加工及检验设备等联动起来,能够实现工件在生产过程中的自动抓取、上料、下料等工艺过程,能够极大的节约人工成本,提高生产效率。
Part.2 行业痛点
1、为应对小批量多品种的生产需求,需设计制作大量的工装夹具,设计制作成本高且无法满足产线柔性化要求。
2、为满足后续工序需要,要求工件有更精确的空间姿态。
3、机械加工车间生产环境恶劣,高温闷热、高噪声、腐蚀性化学品、废气粉尘油雾污染、机械伤害隐患、触电隐患等问题,不仅会严重影响员工的身体健康,直接影响生产效率。
4、再加上制造业用工成本剧增,给企业增添巨大负担等。

Part.3 解决方案
3D视觉定位解决方案:活塞、连杆、曲轴、连杆瓦、曲轴瓦、活塞环、钢圈、轮胎等汽车零部件上下料。

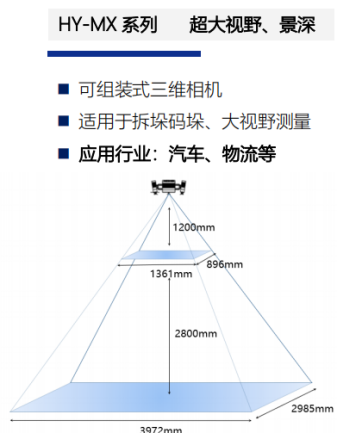
3D视觉定位系统可以通过视觉感知技术实现机器人的自动判断功能。通过使用摄像头和计算机视觉算法,机器人可以感知周围环境并识别物体、场景和动作等,从而能够进行自动判断和决策。
还可以通过使用传感器获取机器人的运动数据和环境信息。从而实现机器人的自动判断功能。使用加速度计、陀螺仪等传感器,机器人可以感知自己的运动状态并做出相应的调整。
最后还可以通过使用人工智能算法进行机器人的自动判断功能。使用深度学习算法,机器人可以学习和识别各种物体和场景,从而能够进行自动判断和决策。
凭借着良好的综合性能,3D视觉定位系统让六轴机械臂已不仅仅只是单一的重复劳动的机器,而是成为了具有自动判断功能的智能搬运机器人。在活塞、连杆、曲轴、连杆瓦、曲轴瓦、活塞环、钢圈、轮胎等汽车零部件上下料过程中,无需人工干预,机器人即实现完整的自动上料、下料循环过程。
