网站怎么做图片链接天津建设协会网站首页
系列文章目录
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- 一、堆的定义
- 二、堆的实现
- 三、堆的接口函数
- 1、初始化
- 2、销毁
- 3、插入
- 4、删除
- 5、判空
- 6、元素个数
- 四、堆排序
- 1、建堆
- 2、排序
- 五、堆的应用——TOPK
- 1、什么是TOPK问题?
- 2、解决方法
- 总结
前言
堆就是完全二叉树。
一、堆的定义
我们了解到了树、二叉树等相关的概念,那么今天所讲解的堆就是基于二叉树中的完全二叉树实现的。那么在完全二叉树的基础上,堆还满足该性质:堆中的子节点始终小于等于(大于等于)父节点。
倘若,堆的父节点始终小于等于其子节点,我们就称之为小根堆。
倘若,堆的父节点始终大于等于其子节点,我们就称之为大根堆。
堆的逻辑结构与物理结构:
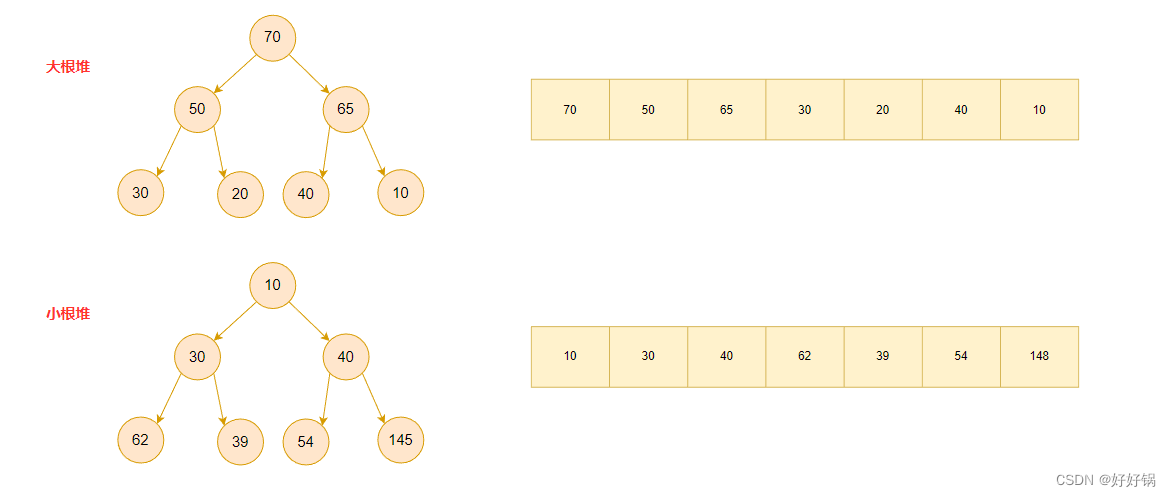
从上述的物理结构我们可以知道,我们接下来的代码实现是基于数组的。因此,我们将采用动态顺序表的思路来存储堆。
二、堆的实现
typedef int HPDataType;typedef struct Heap
{HPDataType* a;int size;int capacity;
}HP;
三、堆的接口函数
1、初始化
void HeapInit(HP* php)
{assert(php);php->size = 0;php->capacity = 4;HPDataType* cur = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HP));assert(cur);php->a = cur;
}
2、销毁
void HeapDestory(HP* php)
{assert(php);php->size = 0;php->capacity = 0;free(php->a);php->a = NULL;
}
3、插入
void HeapPush(HP* php, HPDataType x)
{assert(php);if(php->capacity == php->size){//扩容php->capacity *= 2;HPDataType* cur = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->a, sizeof(HP) * php->capacity);assert(cur);php->a = cur;}php->a[php->size++] = x;AdjustUp(php->a, php->size - 1);}
我们是在最后一个位置插入一个数据,然后再让这个数据向上移动。
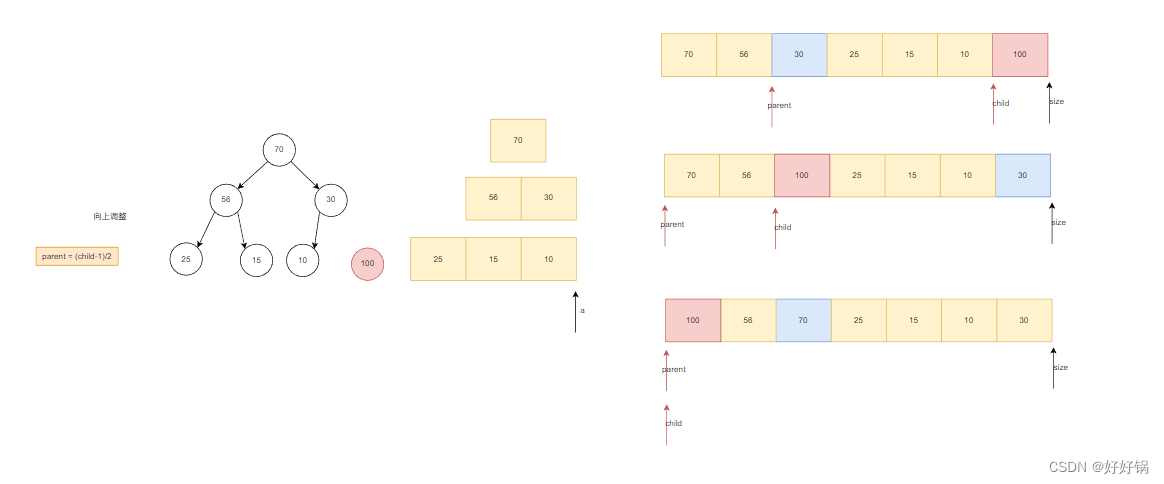
我们发现,100需要向上移动的话,只需要和100的祖宗们相比较。因此,我们可以写出AdjustUp的函数。
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child)
{//向上调整int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0){if (a[parent] < a[child]){swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;}else{break;}}
}
4、删除
void HeapPop(HP* php)
{assert(php);assert(php->size > 0);swap(&php->a[0], &php->a[--php->size]);AdjustDown(php->a, 0, php->size);
}
我们这里需要删除的是堆顶。但数组中删除堆顶元素的时间复杂度是O(N)。这是相当复杂的,而尾删的时间复杂度是O(1),于是我们这里也是先将尾部元素和堆顶元素进行交换,然后再将堆顶元素向下移动。
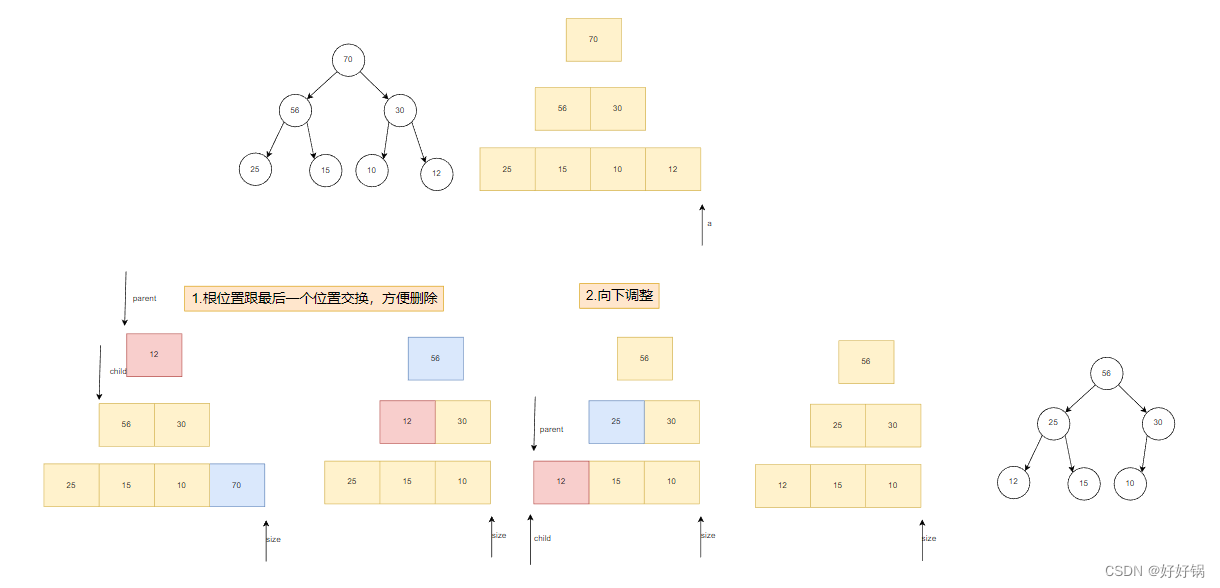
void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a, int parent, int size)
{//向下调整int child = parent * 2 + 1;while (child < size){//确认child指向大的哪个孩子if (child + 1 < size && a[child + 1] < a[child]){++child;}if (a[child] < a[parent]){//孩子大于父亲,交换,继续向下调整swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else{//孩子小于父亲break;}}
}
5、判空
bool HeapEmpty(HP* php)
{assert(php);return php->size == 0;
}
6、元素个数
int HeapSize(HP* php)
{assert(php);return php->size;
}
四、堆排序
1、建堆
堆排序的基础是将数组中的元素建成一个堆:
方式1:尾插
我们从第一个元素开始,不断地插入新元素,然后让这个元素向上调整,让其对应到相应的位置。让数组始终保持一个堆,这样才能向上调整。
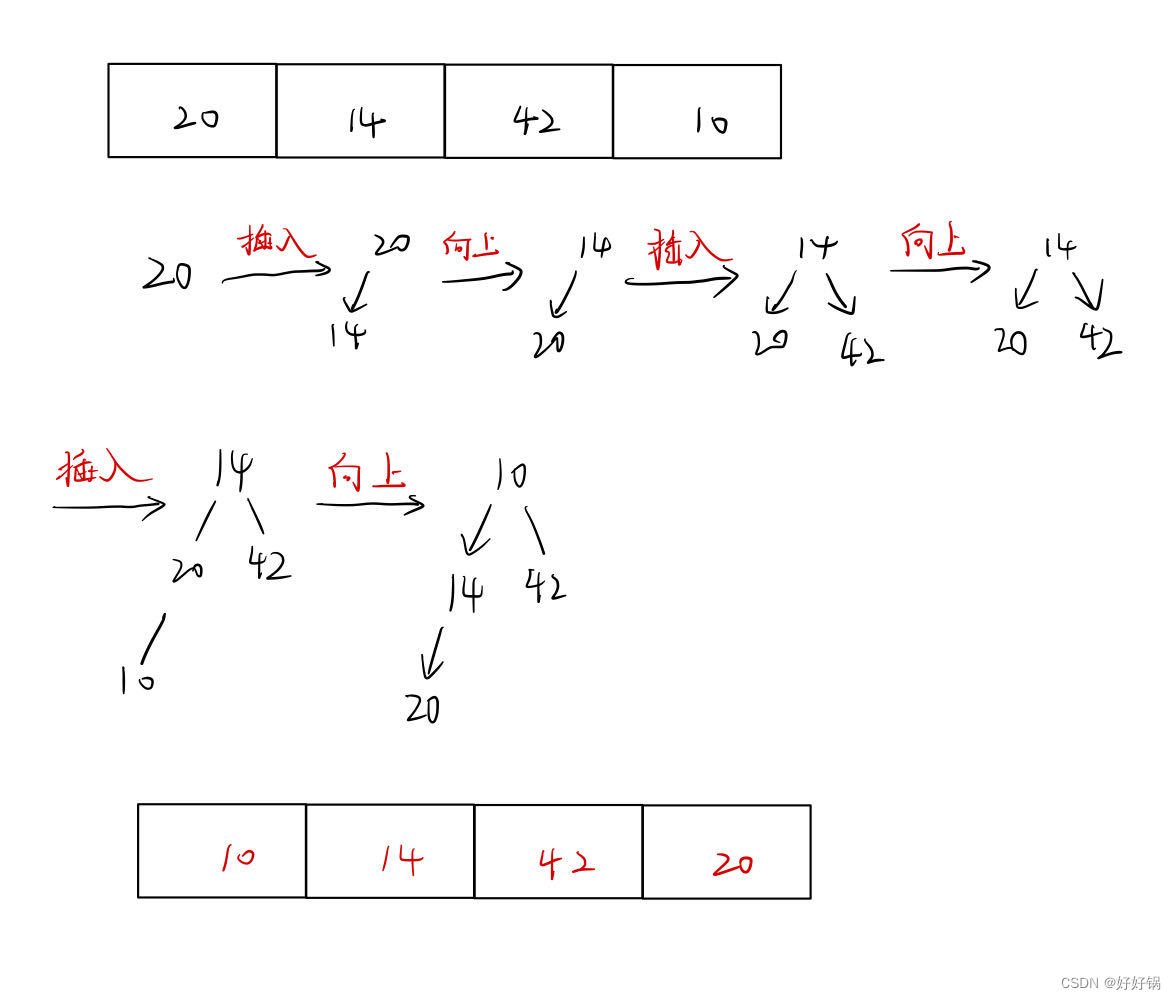
void AdjustUp(int*arr,int child)
{int parent=(child-1)>>1;while(child>0){if(arr[child]>arr[parent]){swap(arr[child],arr[parent]);child=parent;parent=(child-1)>>1;}else break;}
}
void Heap_Sort(int*arr,int size)
{//建堆for(int i=0;i<size;i++){AdjustUp(arr,i);}//.....
}
方式2:根节点向下调整
向下调整一般是针对根节点的,但是向下调整要保证下面紧跟的两个子树是两个堆,否则就会出错。因此,我们可以从倒数第二排开始,不断调整每一个小堆,从小到大,从少到多。
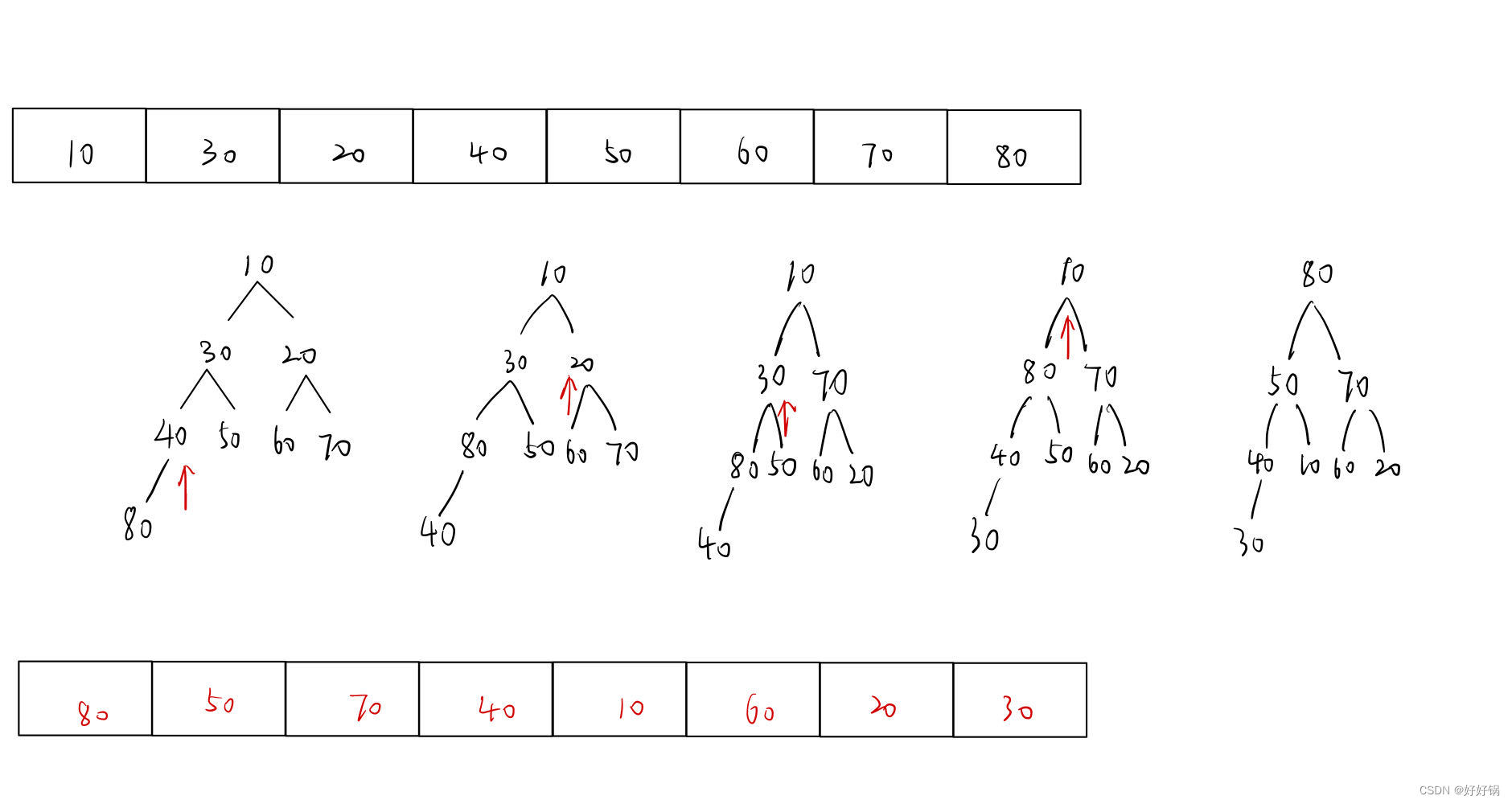
我们先保证两个子树是堆,然后再去调整这个两个子树的根节点。
void AdjustDown(int*arr,int size,int parent)
{int child=parent*2+1;while(child<size){if(child+1<size&&arr[child+1]>arr[child])child++;if(arr[child]>arr[parent]){swap(arr[child],arr[parent]);parent=child;child=parent*2+1;}else break;}
}
void Heap_Sort(int*arr,int size)
{//搭建一个大根堆for(int i=(size-1-1)/2;i>=0;i--){AdjustDown(arr,size,i);}//.........
}
2、排序
排序的话,假设我们是升序排列,但是我们创建的小根堆,那么每次取出根节点,但是取出之后,我们的堆的结构就混乱了,因此我们就需要重新建堆,此时的时间复杂度是n方。
于是我们换一个思路,我们创建一个大根堆,那么根节点就是最大的,我们让根节点和最后一个元素交换,然后我们删掉最后一个元素,即让尾指针前移,此时我们的最大值存储在了数组中的最后一位,然后我们让根节点向下移动,恢复堆的结构,此时堆顶就是次大值,然后我们再交换,让次大的元素到倒数第二的位置。由此类推,最后就能排好所有元素,其顺序为升序。
我们的根节点向下移动的时间复杂度是O(logN),共N个元素,此时时间复杂度是O(NlogN)。
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
void AdjustDown(int*arr,int size,int parent)
{int child=parent*2+1;while(child<size){if(child+1<size&&arr[child+1]>arr[child])child++;if(arr[child]>arr[parent]){swap(arr[child],arr[parent]);parent=child;child=parent*2+1;}else break;}
}
void Heap_Sort(int*arr,int size)
{for(int i=(size-1-1)/2;i>=0;i--){AdjustDown(arr,size,i);}for(int end=size-1;end>0;end--){swap(arr[0],arr[end]);AdjustDown(arr,end,0);}
}
五、堆的应用——TOPK
1、什么是TOPK问题?
topk问题就是,我们再一堆数字中选出前K个最大的或者最小的数字。
2、解决方法
如果我们的数据量是十个亿,此时我们的内存区是不支持将其造成一个堆的,所以我们利用前k个元素创建一个元素个数为k的小根堆,那么我们堆中的较大元素一定会 “沉底”。此时,我们再去不断地读取元素,然后让这个元素和根节点比较,如果大于根节点,我们就替换掉根节点,然后让替换后的新的根节点下沉,为什么让这二者比较呢?因为我们创建的是小根堆,但是我们想要的是最大值,而根节点是最小的,所以根节点是最有可能被换掉的,所以我们让根节点去比较,最终剩下的这个元素为K的堆,就是答案。
// 在N个数找出最大的前K个 or 在N个数找出最小的前K个
void TopK(int* a, int n, int k)
{HP hp;HeapInit(&hp);// 创建一个K个数的小堆for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i){HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);}// 剩下的N-K个数跟堆顶的数据比较,比他小,就替换他进堆for (int i = k; i < n; ++i){if (a[i] < HeapTop(&hp)){HeapPop(&hp);HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);}}HeapPrint(&hp);HeapDestroy(&hp);
}总结
堆是一个逻辑上的完全二叉树,物理上是动态顺序表。
在希望与失望的决斗中,如果你用勇气与坚决的双手紧握着,胜利必属于希望。——普里尼
